Fight Inflammation Naturally: New Cell Type Discovered for Gut-Derived Brain Protection
 Science is continually revealing that inflammation leads to disease, and that might have you looking for foods to fight inflammation (or just a way to fight inflammation naturally) as opposed to taking NSAIDs and other medications that can actually add to the problem.
Science is continually revealing that inflammation leads to disease, and that might have you looking for foods to fight inflammation (or just a way to fight inflammation naturally) as opposed to taking NSAIDs and other medications that can actually add to the problem.
New research has uncovered that a type of cell that was originally thought to be linked to increased inflammation may actually be able to be manipulated to fight inflammation instead. These cells are called astrocytes and in this article, we will cover:
- What are astrocytes?
- What is the role of an astrocyte?
- How do astrocytes protect the brain?
- How do astrocytes contribute to disease and inflammation?
- What foods fight inflammation naturally?
So let’s dive in and find out exactly why these particular cells are so important in the fight against inflammation and how we can best support them!
What are astrocytes?
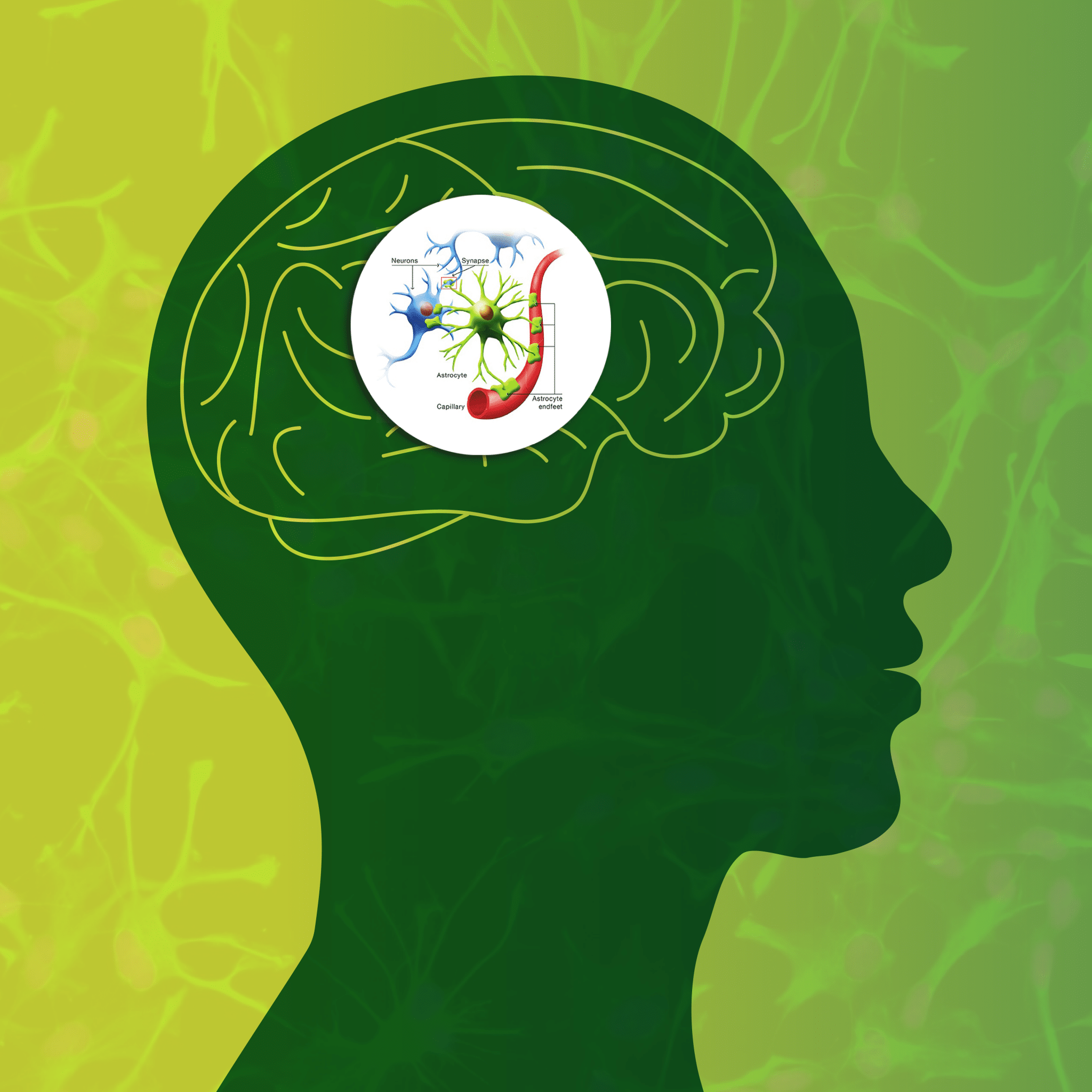
Astrocytes are star-shaped cells that line your entire central nervous system (CNS). Astrocytes are a form of glial cells meaning they don’t create electrical impulses in your brain as neurons do. They were originally considered to just be “nerve glue”. However, research shows us now that they have a much more important job.
Astrocytes aren’t the only glial cells, but they are what we will be focusing on. An astrocytes main job is to maintain a healthy chemical environment for neurons to signal properly.
There are two types of astrocytes:
- Protoplasmic — found throughout your grey matter
- Fibrous — found throughout your white matter
Both types of astrocytes contact with blood vessels and create gap junctions between neighboring astrocytes.
What is the role of an astrocyte?
Astrocytes are important to maintain homeostasis within our CNS. However, that doesn’t tell us much since there are a lot of different moving parts that can get out of balance.
Some of the main jobs of an astrocyte include but are not limited to:
- Balance of glutamate, ion, and water levels
- Scar formation and tissue repair
- Synapse modulation
- Energy storage and mitochondria biogenesis
- Protection against oxidative and nitrosative stress
- Communication with blood vessels and neurons after a CNS injury has occurred
- Clearing out of disease-specific proteins like β-amyloid and α-synuclein
Since astrocytes are found within both white and grey matter they are specifically being targeted to help avoid neurodegenerative diseases.
How do astrocytes protect the brain?
When an injury is perceived in the CNS, the reactive gliosis response is triggered by astrocytes. This response can happen because of several different risk factors, and each one is responded to in its own individual way.
It reacts kind of like your emergency action plan (EAP) at work. Depending on what crisis is happening, you have a set course of actions you need to take so you and others remain safe.
Often the reactive gliosis response will have astrocytes triggering the release of inflammatory molecules like cytokines and chemokines. These molecules are great for acute CNS damage, however, if they are constantly being released they cause damage to the surrounding structures.
 How do astrocytes contribute to disease and inflammation?
How do astrocytes contribute to disease and inflammation?
Since we know that astrocytes can release inflammatory molecules that is one way they are able to contribute to disease. Some of the main diseases that show astrocytic complications include:
- Alzheimer’s Disease
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Huntington’s disease
- Parkinson’s Disease
- Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
It is believed that within all of these diseases, two major things happen with astrocytes:
- They lose their normal homeostatic functions
- They begin having toxic functions within these diseases
So when this happens the astrocytes mutate and change how they operate within your body. They start sending out more inflammatory signals and promote the growth of proteins like β-amyloid and α-synuclein.
Fortunately, it was found that gut microbes can be a key factor in the health or disease of astrocytes.
Astrocytes and Gut Microbes
The gut microbiome is an influential factor in our general health and well-being. Most of our immune system has been found within our gut. The trillions of bacteria that live in our intestines help to break down foods and release metabolites that support our immune function.
Part of this immune system control that our guts have is fighting inflammation.
A lot of the things we are exposed to these days are inflammatory igniters (processed foods, high sugar and sodium, plastics, pesticides, antibiotics, etc.). That means that our inflammatory biomarkers are raised more than what our bodies can handle. Studies show that western-style diets increase inflammation and affect our gut microbes to become unbalanced. This ultimately leads to higher levels of inflammation and disease.
Since our diets can so easily affect these levels negatively, we are also able to see that a positive change in diet can have a positive effect as well.
A specific type of astrocyte and gut-derived metabolite were found to be pivotal in dealing with MS symptoms. The metabolite found was derived from tryptophan.
Side information about tryptophan: You may be familiar with tryptophan as the reason you get sleepy after your Thanksgiving Day meals. Tryptophan is found in protein-filled foods like turkey, nuts, and milk. Tryptophan is often promoted for improved sleep quality and mood balancing.
The tryptophan metabolite communicated directly to the astrocytes through the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR). The metabolite signaled for the astrocytes to reduce CNS inflammation and was successful.
This same AhR is a pathway being studied to help patients with irritable bowel disease (IBD). This has opened the door to more research to find other metabolites that can affect autoimmune and inflammatory disorders.
The main goal here is to reduce inflammatory biomarkers. Once we are able to reduce inflammation diseases aren’t as difficult to fight.
We kept that at the top of our minds when creating Atrantil. Polyphenols have been proven to have strong antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. Inflammation is the instigator for a lot of diseases and stomach ailments and anyway we can naturally reduce it, is a good thing.
Eating a well-balanced diet, maintaining a consistent light-workout routine, and keeping our stress levels low will help us all to lead better and healthier lives. What do you do to keep inflammation low? Let us know in the comments below!
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK10869/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2799634/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6562853/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4448607/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4448607/#idm139679736643456title
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4899206/#S10title